Raspberry Pi Pico w
Guaranteed Safe Checkout


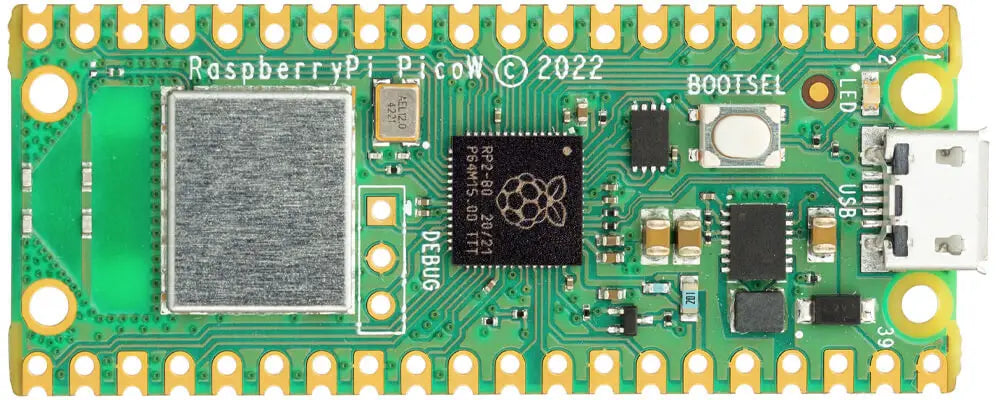
Raspberry Pi Pico w
Following the hugely popular Raspberry Pi Pico, the new Raspberry Pi Pico W is a wireless-enabled version of the RP2040-based board, adding 2.4GHz 802.11n WiFi connectivity!
The addition of wireless connectivity opens up the Pico W to a vast new range of projects such as remote sensor readings, remote control, home automation, mini web servers, wireless GPIO pin control and much, much more!
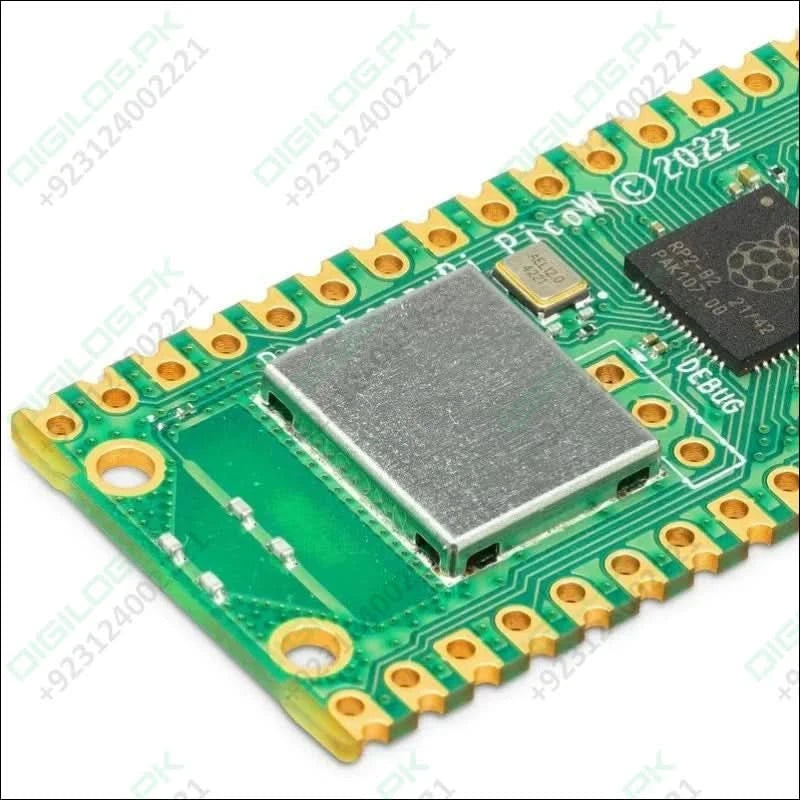
At the heart of the Pico W is the RP2040 – the same chip used in the original Raspberry Pi Pico, featuring two ARM Cortex-M0+ cores clocked at 133MHz; 256KB RAM; 30 GPIO pins; and a broad range of interfacing options. This is paired with 2MB of onboard QSPI Flash memory for code and data storage.
WiFi is enabled via the use of an Infineon CYW43439 wireless chip. The CYW43439 supports IEEE 802.11 b/g/n wireless LAN, and Bluetooth 5.2; however only wireless LAN is software-supported at launch.
With the same footprint and same RP2040 chip, this WiFi Pico can be used as a drop-in replacement for your existing Raspberry Pi Pico projects, upgrading them with WiFi. Just grab a Micro-USB cable (or our handy Pico Essential Kit with a USB cable, headers and more!), install the latest MicroPython Pico W specific U2F file and start programming!
The Pico W can be quickly and easily programmed using MicroPython and C/C++* using popular editors such as Thonny. Learning how to use the Pico and MicroPython is also very easy thanks to the dedicated Getting Started projects and guide. There's also a guide for connecting to the internet with the Raspberry Pi Pico W.
A Raspberry Pi Pico WH version, with a 40-way header pre-soldered, will also be available, however not at the initial launch (estimated availability August/September 2022).
*Initially, Wi-Fi connectivity will be supported by MicroPython only. C/C++ support is on the way (timescales not yet known).
Raspberry Pi Pico W Specifications
The main chip on board is the RP2040 made by Raspberry Pi (their first in-house microcontroller chip!) and is a dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ processor, with a flexible clock running up to 133MHz. WiFi is enabled via the use of an Infineon CYW43439.
- RP2040 microcontroller chip designed by Raspberry Pi in the United Kingdom
- Dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ processor, flexible clock running up to 133 MHz
- 264kB of SRAM, and 2MB of onboard Flash memory
-
Infineon CYW43439 wireless chip
- IEEE 802.11n wireless LAN
- Bluetooth 5.2 (not software supported at launch)
- WPA3
- SoftAP (up to 4 clients)
- Onboard antenna licenced from ABRACON (connected via SPI to the RP2040)
- Castellated module allows soldering directly to carrier boards
- USB 1.1 Host and Device support
- Low-power sleep and dormant modes
- Drag & drop programming using mass storage over USB
- 26 multi-function GPIO pins
- 2×SPI, 2×I2C, 2×UART, 3×12-bit ADC, 16×controllable PWM channels
- Real-time clock (RTC)
- Temperature sensor
- Accelerated floating-point libraries on-chip
- 8×Programmable IO (PIO) state machines for custom peripheral support
- Dimensions (WxLxH)
- Pico W: 21mm x 51.3mm x 3.9mm
- Pico WH: 21mm x 51.3mm x 12.9mm
- Weight
- Pico W: 4g
- Pico WH: 6g
- Country of origin
- Pico W: Japan
- Pico WH: Great Britain
- Product number:
- Pico W: SC0918
- Pico WH: SC0919
Raspberry Pi Pico W Accessories
We have a great range of Raspberry Pi Pico accessories and add-ons available in our Pico section! You can also read about our favourite Pico add-ons and accessories here!
Raspberry Pi Pico W Resources
- Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Pico
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Pinout
- Connecting to the internet with the Raspberry Pi Pico W
- MicroPython UF2 image with networking support
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Datasheet
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Product Brief
- Raspberry Pi Pico W STEP 3D Model
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Fritzing part
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Design Files
- Infineon CYW43439 datasheet
- Thonny Python IDE
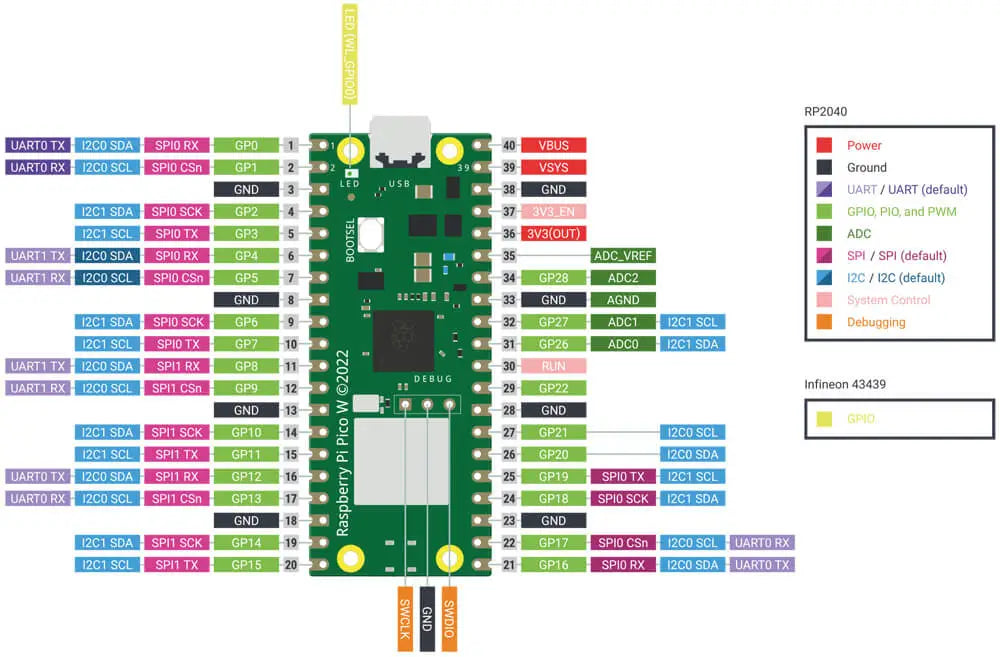
Raspberry Pi Pico W Pinout
A few RP2040 GPIO pins are used for internal board functions:
- GPIO29 OP/IP wireless SPI CLK/ADC mode (ADC3) to measure VSYS/3
- GPIO25 OP wireless SPI CS - when high also enables GPIO29 ADC pin to read VSYS
- GPIO24 OP/IP wireless SPI data/IRQ
- GPIO23 OP wireless power on signal
- WL_GPIO2 IP VBUS sense - high if VBUS is present, else low
- WL_GPIO1 OP controls the on-board SMPS power save pin (Section 3.4)
- WL_GPIO0 OP connected to user LED
Apart from GPIO and ground pins, there are seven other pins on the main 40-pin interface:
- PIN40 VBUS
- PIN39 VSYS
- PIN37 3V3_EN
- PIN36 3V3
- PIN35 ADC_VREF
- PIN33 AGND
- PIN30 RUN
Raspberry Pi Pico W FAQs
What differences are there between the original Raspberry Pi Pico and the new Pico W?
The main changes are:
- The Pico W includes the wireless Infineon CYW43439 wireless chip
- The Pico W has a different component layout, including debug pins moved to the middle of the board
- The onboard LED, Power Supply Mode Select and VBUS Detect pins are now controlled via the wireless LAN chip
What else do I need to use a Raspberry Pi Pico?
- You'll need a micro-USB cable to allow you to connect it to your computer or Raspberry Pi for programming
- You may want to purchase a header set to allow you to use the Pico W with a breadboard, or select the Pico WH version instead (soldering your own headers allows you to choose the format or colour)
- There's also the excellent Get Started with MircoPython on Raspberry Pi Pico book for learning how to use the Pico
What can I use the new Wi-Fi connectivity for?
Any project that uses input to a GPIO pin to trigger an action in your code can be performed remotely via a WiFi connection, opening up the Pico to thousands upon thousands of new project possibilities!
This can be via a small web server running on the Pico W itself, which is covered in the Connecting to the internet with Raspberry Pi Pico W PDF. There will be many more projects and uses as the Pico W makes its way out to the creative community, and no doubt many IoT services will adopt the Pico W too. The Raspberry Pi forum Pico section is a great place to watch for new projects and ideas!
What WiFi frequency does the Raspberry Pi Pico W support?
The Pico W runs on 2.4GHz networks.
The Pico W doesn’t work (or works slowly) on my WiFi network, why?
Whilst we’re still learning about the new Pico W, many similar boards sometimes struggle with mesh networks or advanced networks that automatically switch between the 5GHz and 2.4GHz frequencies. Try restricting your network to 2.4GHz only (see your router datasheet/manual for instructions). Your 2.4GHz network may also be on a 'busy' local band with many other routers in your area, try analysing your local band traffic and switching bands (and/or set a static band and turn off auto band switching).
How does the onboard LED work on the Raspberry Pi Pico W?
Unlike the original Pico W, the onboard LED on Pico W is not connected to GP25 on the RP2040, but instead to a GPIO pin on the wireless chip. MicroPython has been modified accordingly and official Raspberry Pi documentation will detail how to use the onboard LED on the Pico W.
Do I need a different MicroPython UF2 for the Pico W?
Yes! You’ll now find two versions of the UF2 file on Raspberry Pi’s website, one for the original Pico/Pico H, and another for the Pico W/WH
Does the Raspberry Pi Pico W use more power than the original?
We expect so, but no official information has been released on this yet. Watch this space!
I need help using the Pico W, where can I go?
If you need help with your Pico W project or using the new WiFi functionality, the datasheet and other official Raspberry Pi documentation are a great place to start. If you can’t find what you need in the official documentation, search for your question on the Raspberry Pi forum or create a new post if you can’t find what you need.
Customer questions & answers
Ask a question
No questions yet. Be the first to ask!